Table of contents
Introduction-
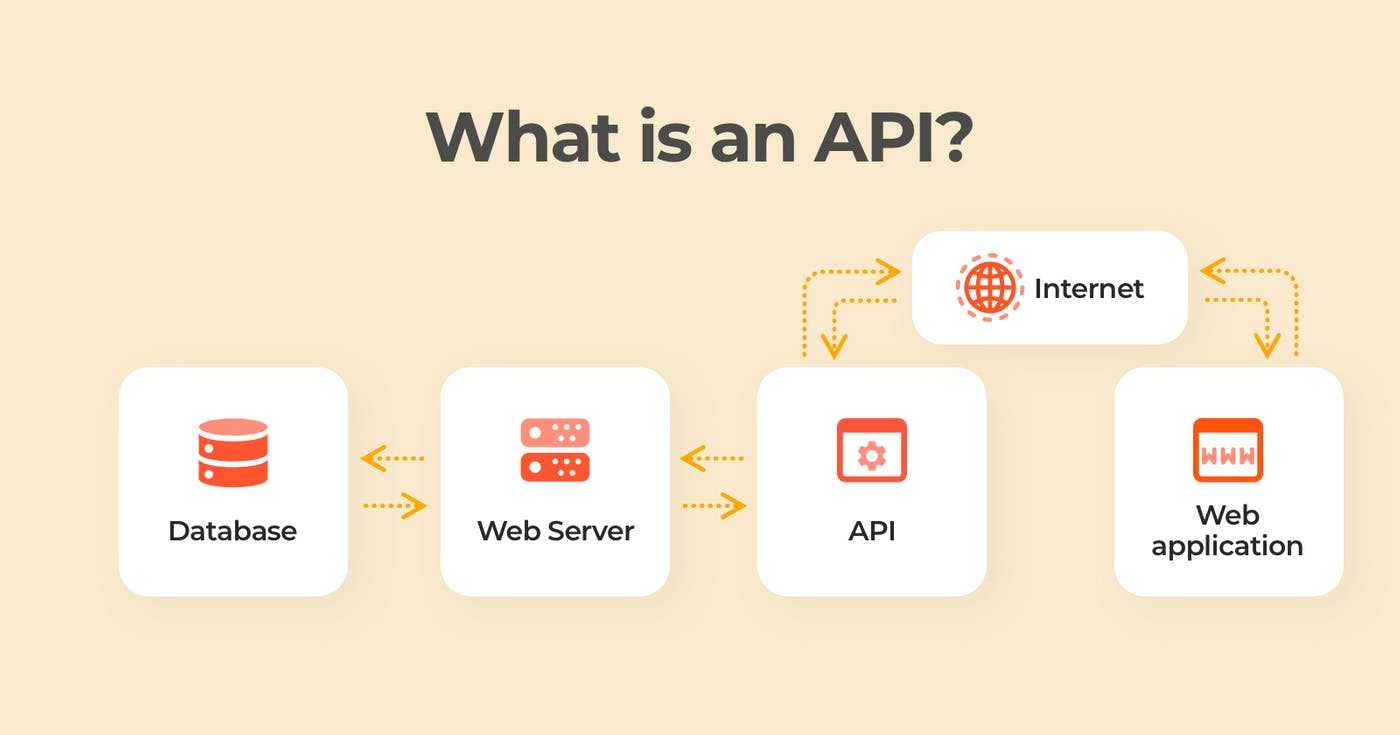
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software.[1] A document or standard that describes how to build or use such a connection or interface is called an API specification. A computer system that meets this standard is said to implement or expose an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation.
How do APIs work?
APIs let your product or service communicate with other products and services without having to know how they’re implemented. This can simplify app development, saving time and money. When you’re designing new tools and products—or managing existing ones—APIs give you flexibility; simplify design, administration, and use; and provide opportunities for innovation.
APIs are sometimes thought of as contracts, with documentation that represents an agreement between parties: If party 1 sends a remote request structured a particular way, this is how party 2’s software will respond.
Because APIs simplify how developers integrate new application components into an existing architecture, they help business and IT teams collaborate. Business needs often change quickly in response to ever shifting digital markets, where new competitors can change a whole industry with a new app. In order to stay competitive, it's important to support the rapid development and deployment of innovative services. Cloud-native application development is an identifiable way to increase development speed, and it relies on connecting a microservices application architecture through APIs.
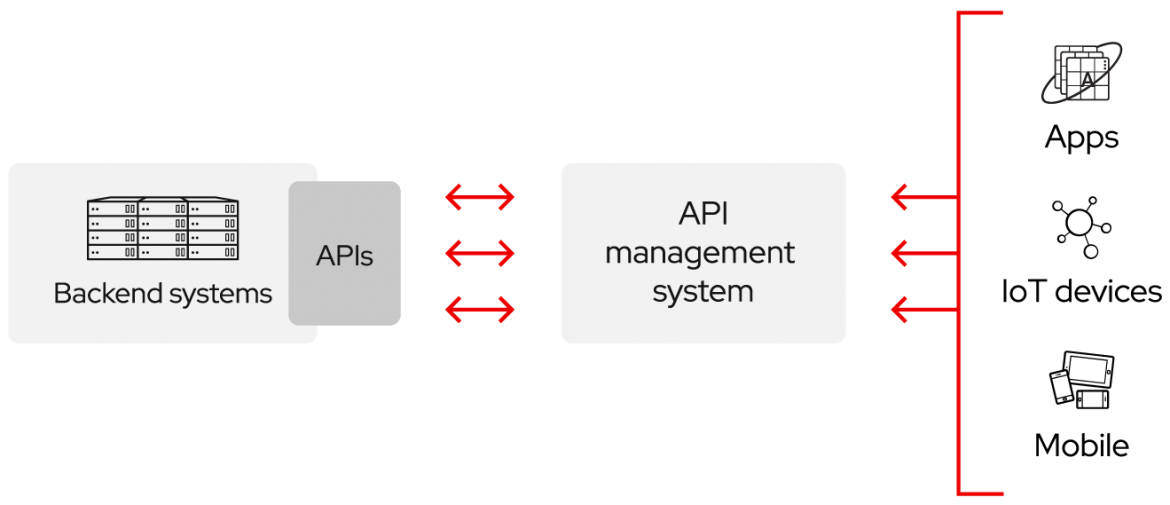
APIs are a simplified way to connect your own infrastructure through cloud-native app development, but they also allow you to share your data with customers and other external users. Public APIs represent unique business value because they can simplify and expand how you connect with your partners, as well as potentially monetize your data (the Google Maps API is a popular example).
For example, imagine a book-distributing company. The book distributor could give its customers a cloud app that lets bookstore clerks check book availability with the distributor. This app could be expensive to develop, limited by platform, and require long development times and ongoing maintenance. Alternatively, the book distributor could provide an API to check stock availability. There are several benefits to this approach:
Letting customers access data via an API helps them aggregate information about their inventory in a single place. The book distributor can make changes to its internal systems without impacting customers, so long as the behavior of the API doesn’t change.
With a publicly available API, developers working for the book distributor, book sellers or third parties could develop an app to help customers find the books they’re looking for. This could result in higher sales or other business opportunities.
In short, APIs let you open up access to your resources while maintaining security and control. How you open access and to whom is up to you. API security is all about good API management, which includes the use of an API gateway. Connecting to APIs, and creating applications that consume the data or functionality exposed by APIs, can be done with a distributed integration platform that connects everything—including legacy systems, and the Internet of Things (IoT).